| Introduction |
| Environmental Issues in LA |
| Mexico |
| Central America |
| Caribbean |
| Guiana Highlands |
| Andean Region |
| Brazil |
| Southern Cone |
| Future |

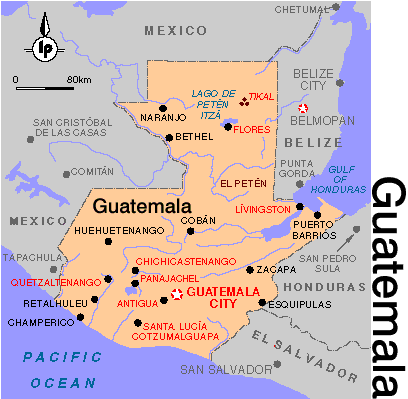
Guatemala
Guatemala is a country south of Mexico which
is made up of plains, highlands and Pacific lowlands. Agriculture
is a major source of economic income for the inhabitants of Guatemala.
However, the country is also made up of many forests which boast cedrela
and mahogany trees, among others. Thus along with many other Latin American
countries, Guatemala also deals with deforestation due to it's rich source
for logging companies and due to farmers needing to clear land for crops
and other such agriculture. As with other countries, if Guatemalans
can get a good price for exporting their crops then they will see it as
more profitable to clear forests for fields than to preserve those forests.
![]()
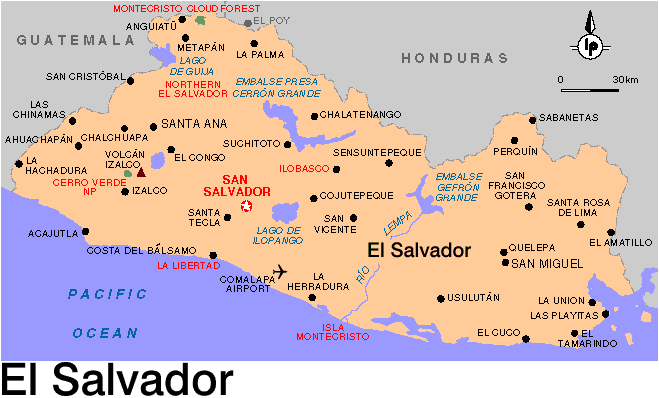
El Salvador
A small country located between Guatemala
and Honduras, El Salvador is composed of coastal lowlands, a central region
and further interior highlands. The economy of El Salvador makes
most of its profit through agriculture because of the extremely fertile
soil found in that region, although small deposits of gold and silver can
also be found in El Salvador.
![]()
Honduras
Honduras’ geography is made up of mountains,
two coastal areas and a plain. Honduras’ main agricultural crops
which are the major exports of the region are bananas and coffee.
Because of the country’s dependence on farming, deforestation and habitat
subsistence are major environmental issues. Honduras deals with soil
erosion and water pollution on a daily basis. The indigenous peoples must
continually fight for soil rights so that they do not lose the environment
upon which they have traditionally been do dependant. Historically,
however, the indigenous peoples are not allowed many land rights and thus
their mere way of life is being threatened by the envirnmental destruction
going on in Honduras.
Links:
TED
Case Studies: Honduras and Deforestation http://gurukul.ucc.american.edu/ted/HONDURAS.HTM
This informative site explores the case
of deforestation within the protected area of the Rio Platano Biosphere
Reserve (RPBP). This are is being logged mainly for its mahogany
trees. The reserve is home to many animal species which survive only
within these tropical and pine forests. The indigenous people living
in the area are fighting to keep the forest in tact.
Honduras
This Week
http://www.marrder.com/htw/special/environment/
This online magazine explores issues related
to the environment in Honduras such as dam projects, NGO protection propositions,
commercial fishing problems, mahogany and mangrove destruction and endangered
species living in Honduras.
Honduras:
Adventures in Nature
http://www2.planeta.com/mader/ecotravel/center/honduras/hond.html
This site lists environmental contacts for
Honduras in government, environmental groups, academic circles, and the
media as well as international environmental contacts.
EI
Projects (South America)
http://www.envintl.com/south-america.html
This site lists projects which Environment
International, Ltd. is taking on throughout South America. Some of
the countries mentioned are Honduras, Costa Rica, Argentina, Bolivia and
Brazil. This company deals mainly with environmental training and
seminars in these various countries which deal with such issues from pesticide
use to environmental law.

The Tigra National Park
Courtesy of: http://www.ctcd.cc.tx.us/students/student08/index.htm
![]()
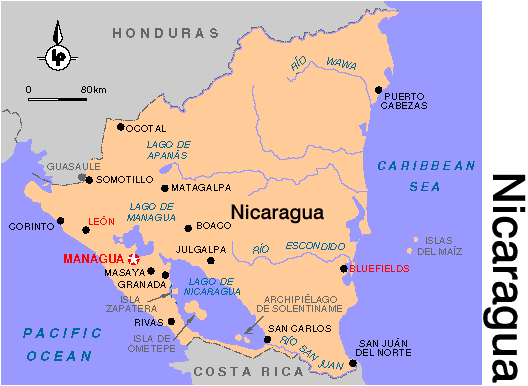
Nicaragua
Nicaragua, a country with two coastal regions
as well as highlands has many farmers because of its fertile soil.
Its main agricultural crops are cotton and coffee. Because of Nicaragua’s
fertile soil it has many forests and thus their biggest environmental concern
is logging.
Many logging companies are vying for rights
to log particular areas of Nicaragua because of the wealth of trees found
there. Although thus far the government of Nicaragua has carefully
reviewed the logging policies of these companies to be certain that they
are environmentally friendly (regarding use of chemicals, pollution and
reforestation), many logging companies do not have policies which live
up to these standards. This is a good thing for the forsets in Nicaragua,
but it is certain that desperate logging companies will one day have a
compromise with the governments will not be able to pass up. The
government of Nicaragua has already been offered large sums of money to
deplete their national debt if the loggers would be allowed to cut down
large areas of forest. One day in the future the offer may be too
good to resist and although the plans for reforstation may not be as adequate
and the government hopes, they may jump at the offer. Thus there
must be legislation put in place should that situation ever arise which
protects these forests and sustain the habitats within them.
Links:
Preserve
Rainforests, Stop Logging
http://www.nativeweb.org/saiic/actions/urgent17.html
This site deals with the Indigenous response
(as of 1998) to logging which is taking place in rainforest lands which
the Sumo and Miskito Indian traditionally used. However, the Indians
do not actually own these lands, and until they do the government may do
whatever they choose with the forests. The main concern with the
logging company is the uprooting of the Indian communities and the pollution
of the water from the chemicals the loggers use.
Nicaragua
Wood Sale to Taiwan
http://gurukul.ucc.american.edu/ted/NICARAG.HTM
This site is actually a case study of another
logging company trying to get a hold of the wood in Nicaragua. The
opposition to the deal are again the Moskito Indians who live in the proposed
area. The appeal the government had to the deal were the 4,000 jobs
it would have created in the area (which has a rate of unemployment at
80%), the US$15 million to be invested in the country during the project
and the loan of US$30 million from Taiwan to help Nicaragua with its foreign
debt. Although this plan was rejected, it raises the problems which
face all sides of the argument: the government needs money and to boost
the economy by providing jobs, the Moskito Indians are upset by the government’s
ignorance of heir rights, and environmentalists are concerned with major
deforestation.
The
Nicaragua Canal Proposal
http://gurukul.ucc.american.edu/ted/NICCANAL.HTM
This case study explores the possibility
of a canal being built through Nicaragua. The US must give control
of the Panama Canal to Panama by December 31, 1999, and there are concerns
over the political aspect as well as the size of the canal which even now
does not allow for certain sized ship to pass through. Although other
options are still be debated at this point, Nicaragua seems like a likely
solution to the many issues at hand with the canal. However, the
construction of a canal would mean more deforestation, mixing of water
from the Atlantic, Pacific and Lake Nicaragua which would negatively affect
ecosystems, and pollution as well would become a problem.
![]()
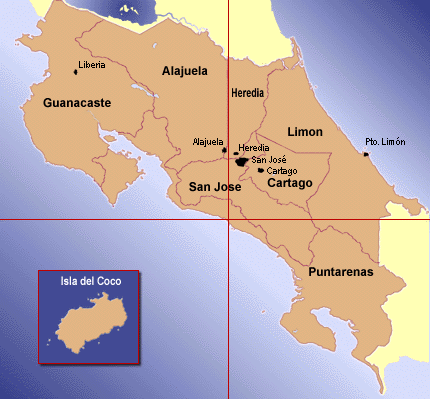
Costa Rica
The geography of Costa Rica is made up of
highlands, lowlands, and coasts. Deforestation is a major problem
because from the fertile soil poring up great forests. The inhabitants
of Costa Rica depend heavily on farming and exporting items such as bananas,
beef, cacao and coffee, so clearing land for crops is a major problem in
Costa Rica as well.
Like Guatemala, Costa Rica gets great prices
for the exports of its agricultural crops, which include beef. These
monetary offers from countried like the United States seem much better
than the money the peoples of Costa Rica could make preserving their land
and lending it out for enterprises such as ecotourism. Although ecotourism
is in thory a viable option for Costa Rica because of its extensive rainforests,
it is also an unrelable source of income. Until another option becomes
just as lucrative, farmers in Costa Rica as well as other countries will
continue to depend on farming and agriculture for their cash.
Links:
TED
Case Studies: Costa Rica Beef Exports
http://gurukul.ucc.american.edu/ted/COSTBEEF.HTM
This case study explores the impact of the
expansion of cattle ranching on deforestation. Because of the price
countries like the US will pay for beef, Cattle ranching has become a profitable
source of income in Costa Rica. Thus expansion of these ranches became
profitable and soil erosion has become a problem. Various solutions
are examined in this case study as well.
TED
Case Studies: Pesticide Hazard in Costa Rica
http://gurukul.ucc.american.edu/ted/COSTPEST.HTM
This case studies the effect a pesticide
DBCP is having on the people and environment in Costa Rica. A pesticide
banned for the use in the United States, DBCP was exported to third world
countries. However, many environmental problems have been reported
and 1,500 workers in Costa Rica have reported sterilization form using
the product. These workers are suing the US companies for compensation
for the damage the product caused.

Image courtesy of: Costa Rica Tours at http://www.costaricatour.com/
Conservation
http://photo.net/cr/moon/conservation.html
This website explores logging and commercial
agriculture’s effects in Costa Rica. It tells how, although the export
of many trees were banned, at night these trees are sneaked out of the
country anyway. The site also explores various governmental attempts
at reforestation and other policies including eco-tourism.
![]()
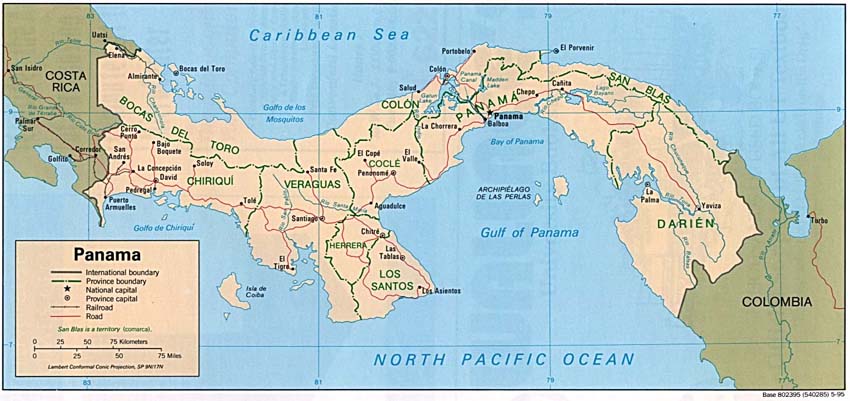
Panama
Panama depends primarily on the Panama Canal
and its center of trade. Made up of central highlands and coastal
lowlands, agriculture is maintained by about a quarter of the population
for subsistence. Panama, like many South American Countries, faces
deforestation as its major environmental problem.
Deforestation often leads to soil erosion,
a major problem in Panama. Once the forests are cleared away, the
soil underneath (since it is used to being sheltered for so long, the topsoil
is only a very thin layer of nutrient-rich soil), is easily washed away
once the rains come. And although at first the soil is very good
for planting crops, eventually the top soil will be eroded away and the
farmers will have to clear another plot of land to yield better results.
Panama
Canal Watershed Under Strain
http://www.foreignwire.com/canal.html
This article deals with deforestation and
its effect of soil erosion, which allows silt to get into the drinking
water and dams to be backed up, and the fact that farming in the only mainstay
for may people, and clearing what is left of the land to do so.

Image courtesy of: Panamá: Places,
Folklore, Festivals, and Museums at http://gringo.ent.ohiou.edu/%7Emedina/panama.html
Sources:
The Lonely Planet
http://www.lonelyplanet.com.au/dest/cam/graphics/map-gua.htm
The Lonely Planet
http://www.lonelyplanet.com.au/dest/cam/graphics/map-els.htm
Honduras
http://city.net/maps/view/?mapurl=/countries/honduras
The Lonely Planet
http://www.lonelyplanet.com.au/dest/cam/graphics/map-nic.gif
Costa Rica
http://supersite.incostarica.net/centers/info/maps/
Latin Synergy
http://www.latinsynergy.org/panamamap.htm